Lehtonen, Päivi; Martinsuo, Miia: Integrating the change program with the parent organization; in: International Journal of Project Management, Vol. 27 (2009), No. 2, pp. 154-165.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2008.09.002
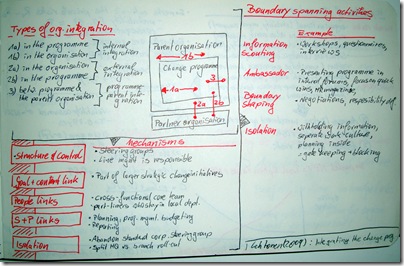
Lehtonen & Martinsuo analyse the boundary spanning activities of change programmes. They find five different types of organisational integration – internal integration 1a) in the programme, 1b) in the organisation; external integration 2a) in the organisation, 2b) in the programme, and 3) between programme and parent organisation.
Furthermore they identify mechanisms of integration on these various levels. These mechanisms are
| Mechanism of integration | |
| Structure & Control | Steering groups, responsibility of line managers |
| Goal & content link | Programme is part of larger strategic change initiative |
| People links | Cross-functional core team, part-time team members who stay in local departments |
| Scheduling & Planning links | Planning, project management, budgeting, reporting |
| Isolation | Abandon standard corporate steering group, split between HQ and branch roll-out |
Among most common are four types of boundary spanning activities – (1) Information Scout, (2) Ambassador, (3) Boundary Shaping, and (4) Isolation. Firstly, information scouting is done via workshops, interviews, questionnaire, data requests &c. Secondly, the project ambassador presents the programme in internal forums, focuses on quick wins and show cases them, publishes about the project in HR magazines &c. Thirdly, the boundary shaping is done by negotiations of scope and resources, and by defining responsibilities. Fourthly, isolation typically takes place through withholding information, establishing a separate work/team/programme culture, planning inside; basically by gate keeping and blocking.